AIAA Houston Section Astrodynamics technical committee
The American Institute of Aeronautics and Astronautics (AIAA)
Technical committee Chair: Dr. Albert Allen Jackson IV
(Here is a link to the News section of this web page. Otherwise, scroll down for that section.)
[April 26, 2024: A Lunch and Learn in the NASA/JSC community by Dr. Albert Allen Jackson IV, “The Interstellar Ramjet: A Technical History”
Date: Friday, April 26,2024
Time: 11:30 AM – 1:00 PM
Place: A hybrid event with Google Meet and the venue NASA/JSC Gilruth Center Lone Star Room, Room #217, 18600 Space Center Blvd, Houston TX 77058.
Details: Please use this link to see more details.
[March 20, 2020: A new article by Dr. Jackson published in JBIS, the Journal of the British Interplanetary Society] “A Neutrino Beacon,” A. A. Jackson, Triton Systems LLC, 17000 El Camino Real, Houston Texas USA 77058. Here is a link to the PDF file.
[July 19, 2019: Apollo 11, the 50th Anniversary] Please enjoy the signed-for-Al-Jackson Apollo 11 crew portrait below (link to our highest resolution version of the portrait here), a souvenir belonging to Dr. Jackson. He was a NASA Manned Spacecraft Center (named Johnson Space Center since February 19, 1973) civil servant for five years during the Apollo program. As we can see, those five years included the Apollo 11 mission. On July 18, 2019, the Paul Gilster Centauri Dreams blog published an article by Dr. Jackson, “Lunar Landing Backup: Apollo’s Abort Guidance System“. Here is a link to that article. We can see that in the photograph, AGS refers to the Lunar Module Abort Guidance System. Reminders: Apollo 11 dates: Launch, July 16, 1969; Landing on the Moon, July 20, 1969; Splashdown, July 24, 1969.
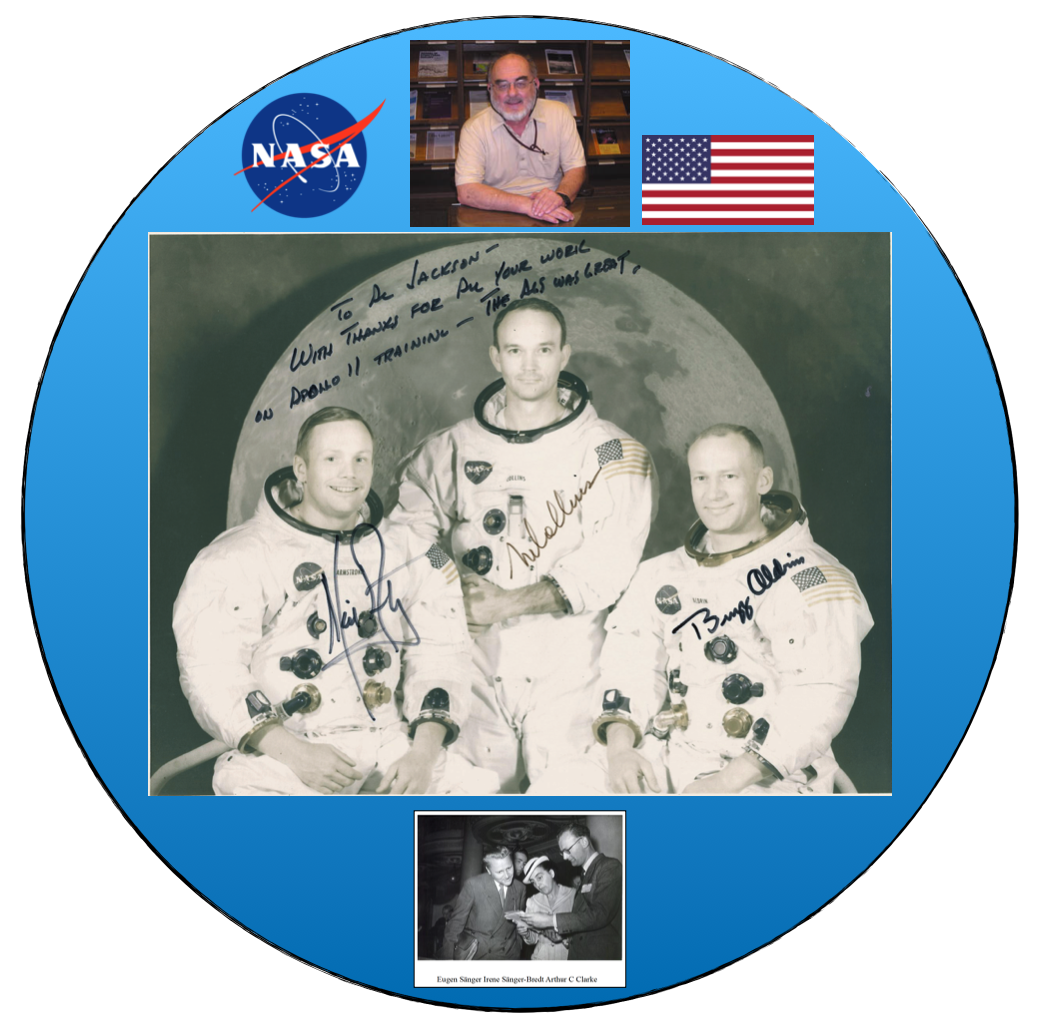
Adding a bit of color to the Apollo 11 crew portrait. All three astronauts signed that portrait for Al Jackson. (Click to zoom.)
[June 22, 2019, Douglas Yazell] An update about published papers and conferences attended by Dr. Jackson.
- Publications:
- May 2019: A Gravitational Wave Transmitter, A. A. Jackson (Triton Systems Houston Texas) & Gregory Benford (Department of Physics & Astronomy, UC Irvine), Journal of the British Interplanetary Society (JBIS, first published in 1934, now monthly), Volume 72 2019, Pages 62-69. Here is a link to that document (PDF).
- June 2019: A Neutrino Beacon, A. A. Jackson, Triton Systems, 17000 El Camino Real, Houston TX 77058. Here is a link to that document (PDF).
- Conferences
- June 27-30, 2019, Foundations of Interstellar Studies Workshop, Charfield, United Kingdom. Here is a link to the program document. Dr. Jackson will present publication #2 above, Neutrino Beacons for Interstellar Communications.
- News articles:
- May 20, 2019, by Universe Today (about a publication by Dr. Jackson), https://phys.org/news/2019-05-advanced-civilizations-neutrino.html
- May 17, 2019, A Neutrino Beam Beacon, by Paul Gilster of Centauri Dreams (blog: Imagining and Planning Interstellar Exploration), about a publication by Dr. Jackson, https://www.centauri-dreams.org/2019/05/17/a-neutrino-beam-beacon/
- Here is a link to the PDF version of the JPEG image below.

Above: JPEG image of this news article, A Status Report of the Astrodynamics Technical Committee (TC) of AIAA Houston Section. (Click to zoom.)
A 2017 Interstellar note from Dr. Albert Allen Jackson IV
To see Dr. Jackson in the group photo below, here is his portrait from the website of the Lunar and Planetary Institute (LPI), downloaded June 19, 2017:

Above: A portrait of Dr. Allen Albert Jackson IV from the website of the Lunar and Planetary Institute (LPI) in Houston Texas USA, where he is a Visiting Scientist.

Above: Institute for Interstellar Studies, New York City College of Technology, CUNY, (Click to zoom.)
Dr. Jackson attended the above event and his presentation charts are available below. The event: Foundations of Interstellar Studies, Workshop on Interstellar Flight, City Tech, CUNY, New York, USA, June 13-15, 2017, Institute for Interstellar Studies, New York City College of Technology.
Dr. Jackson has a PDF file (40 pages, 4.3 MB) containing the program and abstracts from the above event. If we obtain permission, we will link to that here. [June 2019. Douglas Yazell. Seems to me we would be OK posting that document here without express permission. Here is a CUNY website / webpage with program details.]
Here is a link to the presentation charts (PDF, 13 pages, 978 KB) created by Dr. Jackson for the above event. Title: Gram-scale Nano-spacecraft Entry into Star Systems. Author, A. A. Jackson, Lunar and Planetary Institute. June 14, 2017. Contact information: al_jackson [at] aajiv.net. Below is a screen capture image of page 1 from that presentation.
2017 event (Lunch & Learn at NASA/JSC Gilruth Center):
Date: Friday, January 27, 2017
Time: 11:30 AM – 1:00 PM
Place: NASA/JSC Gilruth Center Lone Star Room
Subject: Reproducing an Apollo Applications Program Single-Launch Human Venus Flyby Trajectory
Speaker: Daniel R. Adamo, Astrodynamics Consultant
Here is a link to the publicity flyer (PDF). Here is a link to EventBrite web page.
The Adamo Archive in Astrodynamics
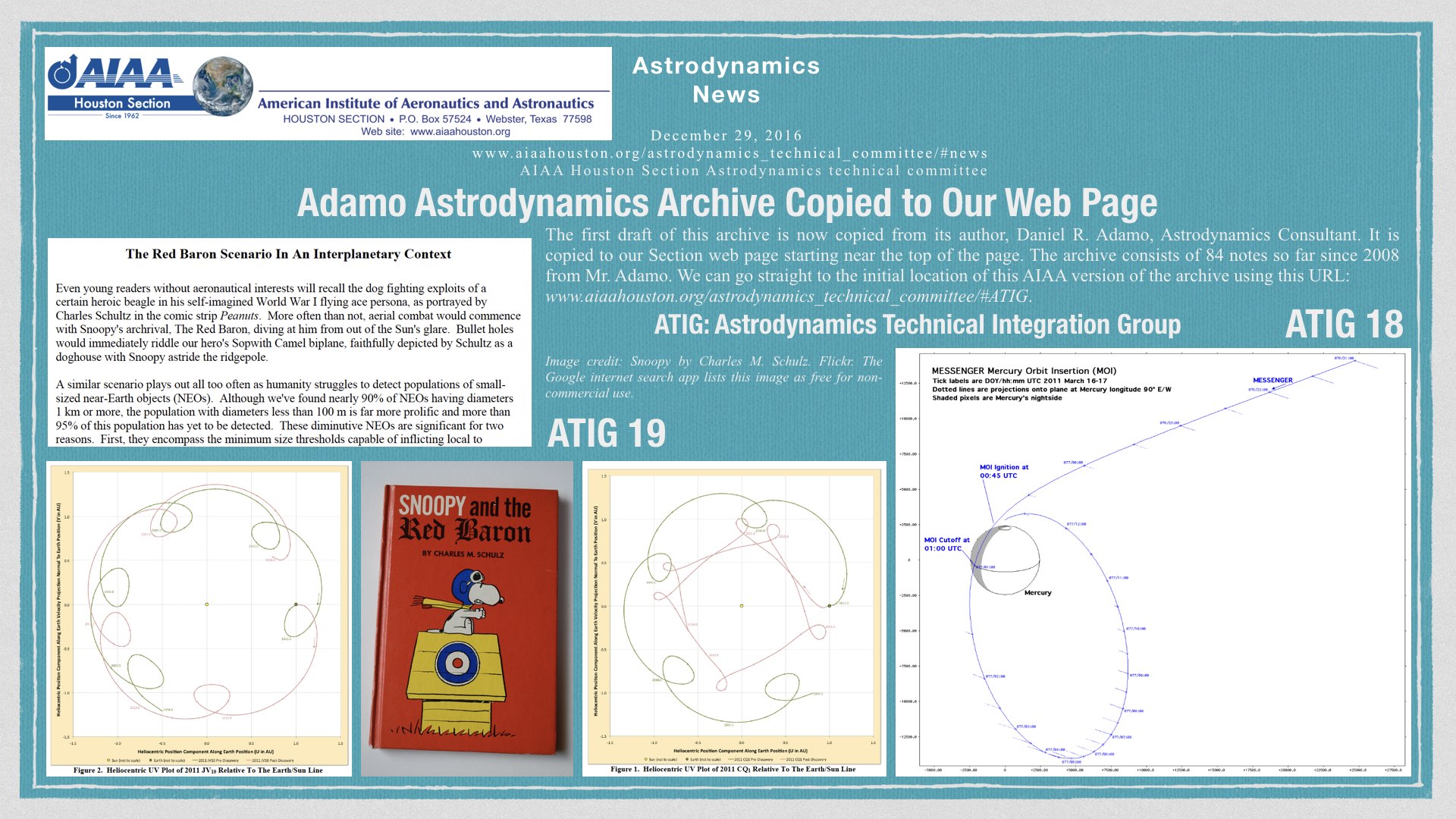
[Update, June 19, 2017] The AIAA copy of this Adamo ATIG (Astrodynamics Technical Integration Group) archive is now stored in its more permanent location (URL): http://www.aiaahouston.org/adamo_astrodynamics/. This new link is also found by surfing to our Section web page, then using menu choices Technical Activities/Daniel R. Adamo Astrodynamics. This AIAA copy of the archive is a big project (thanks very much to all who made it possible and all who worked on it!) of this technical committee (TC, astrodynamics in this case) in our Section. Please search this TC web page for Snoopy or the Red Baron to find a related news article. [End update of June 19, 2017]
Members of the AIAA Houston Section astrodynamics technical committee
- Dr. Albert Allen Jackson IV, Chair
- Associate Fellow, AIAA
- Fellow, British Interplanetary Society
- Senior Member, American Astronautical Society
- NASA civil servant: 5 years in the Apollo program, Lunar Module Simulator instructor, Abort Guidance System and Primary Guidance and Navigation system. MacDonnell Douglas, Computer Science Corporation, Lockheed: Flight planning software, Orbit debris and Engineering Simulation, 40 years.
- Douglas Yazell volunteered in 2015 to create an oral history document here about the career of Dr. Jackson, to be placed here and on the AIAA Houston Section history technical committee web page.
- Dr. Jackson was a team member on a ten-year software project which won second place in 2014 in a NASA competition. Of all the NASA awards in his decades-long career in the NASA/JSC community, this is the only one that included a cash prize.
- March 2015: Dr. Jackson penciled in a Lunch-and-Learn presentation about Traversable Wormholes with himself as the speaker. The movie Interstellar is still talked about in the press and is still in theaters, so that movie might create some interest in this subject.
- Douglas Yazell, Honeywell aerospace engineering 1981-2011 (mostly NASA projects), Horizons newsletter editor 2011-2014, Math Teacher in public high schools, 2016 – present (June 2019). My most recent assignment in Lamar High School in Houston ISD at River Oaks Blvd and Westheimer Road was a great experience for me, February 7, 2019 – May 31, 2019.
- Dr. Tim Crain, Intuitive Machines
We are always looking for new professional members. Contact information is on the organization chart.
Charter
To provide a forum for exchange of ideas and information regarding the state of the art and the future of astrodynamics. To stimulate education, professional development, and accomplishment by fostering communication and by providing resources.
Goals
- Recruit members for the technical committee and AIAA
- Recruit one technical committee member from each ‘astrodynamics’ company in the NASA/JSC community
- Encourage lectures from government, industry, and universities
- Monitor and contribute to the mirror committee on the national level
- Organize lunch-and-learn sessions in the the Houston Clear Lake area (one to four per year)
- Focus on the technical challenges of the next 3-5 years
- Meet in person three to four times per year, sometimes with national committee
- Interact with other AIAA technical committees (including AIAA Houston Section Annual Technical Symposium [ATS] in May of each year), other professional societies, and universities
- Survey tools and techniques
- Contribute articles to AIAA Houston Section Horizons newsletter
- Initiate and review reports on astrodynamics of missions to Mars, Lagrange points, asteroids and cislunar space
Presentations by Dr. Albert Allen Jackson IV
Extreme SETI (1 MB, PDF, a PowerPoint presentation, 20 pages)
Here is the same presentation (PDF) with an audio transcript added using Post-It notes in the PDF. Download this and open it with the free Adobe Reader application in order to see the Post-It notes. The image of Arthur C. Clarke is updated here on the first slide, since the aspect ratio was distorted in the original presentation.
September 19, 2014, at the 100 Year Starship (100YSS) public symposium, G. R. Brown Convention Center, Houston Texas USA, 3:30 PM
Search for Extraterrestrial Intelligence (SETI) is so well-known that it is barely worthwhile to define it here. See the related newsletter article starting on page 13 of the March / April 2014 issue (36 pages, 5 MB PDF) of Horizons, Detecting Starships. The original title of that article was Extreme SETI, but the Horizons Editor decided to avoid undefined acronyms, following the Yahoo style guide. So Horizons, the newsletter of AIAA Houston Section, was first to publish this Extreme SETI subject as written by Dr. Albert Allen Jackson IV.
The above 20-page presentation is not an AIAA presentation, but we have permission from Dr. Jackson to place his presentation file here.
In work September 25, 2014: I (Douglas Yazell) have an iPhone 5 audio recording of the above 15-minute presentation, missing only the first few words. I volunteer to transcribe it and place that PDF file here. In fact, instead of a PDF file, I can probably add that text to the 20 pages above using Adobe Acrobat Post-In Notes. Putting the audio file here would be useful, too, but it is a long audio file that includes a presentation by another speaker, so editing of that audio file would be required.
Lunch-N-Learns
- [Event date (past): Friday: February 12, 2016]:
- Time: Noon to 1:00 PM
- Place: NASA/JSC Gilruth Center Lone Star room (Maximum capacity: 54 people) Six people per round table.
- Speaker (invited & confirmed): Art Dula (link to the Arthur M. Dula Wikipedia article)
- Subject: Space Mineral Resources, a Global Assessment, Challenges and Opportunities, Art Dula, Editor, a book published in September of 2015 (see the image below)
- Details:
- Link to an EventBrite page for this event
- Link to the event page at www.aiaahouston.org
- Link to the one-page publicity flyer
- Either the EventBrite or the event page link was used to sign up in advance
- Walk-ins were welcome
- Optional lunch meal if ordered and paid for in advance online (Red River BBQ)
- Lunch cost was published on those two web pages
- Free event for those who preferred to attend without buying lunch
- Link to book cover image and editor list
- December 5, 2014
Economics of Asteroid Mining
Shen Ge, Bachelor’s Degrees of Science, Georgia Tech University, Aerospace Engineering & Physics; Master’s Degree of Science, Texas A&M University, Aerospace Engineering.
Location: NASA Johnson Space Center Gilruth Center Coronado Room
Attendance: 16
Link to one slide (one chart) of images for and from this event
Presentation: PDF - June 7, 2010
Exploring Near-Earth Objects (NEOs) with Human and Robotic Systems
Daniel R. Adamo, astrodynamics consultant, Houston, Texas 77059, and Rob Landis, NASA
Presentation: PDF - April 26, 2010
How to Build Cost-Optimized Interstellar Beacons (and How to Search for Them)
James N. Benford, Ph.D., Microwave Sciences, Inc.
Publicity Flier: PDF - November 20, 2009
Apollo 12, the 40th Anniversary, a Panel Discussion
Panelists: Emil Schiesser (MPAD flight planner), Francis E. “Frank” Hughes (simulator trainer), and Floyd Bennett (flight controller)
Publicity Flier: DOC - November 13, 2009
The Japanese Hayabusa Spacecraft with Sample Return from Asteroid Itokawa
Dr. Paul Abell, Lunar and Planetary Institute, Houston Texas
Publicity Flier: DOC - June 12, 2009
A Lunar Surface Rendezvous Architecture Proposal
Daniel R. Adamo, astrodynamics consultant, Houston Texas 77059
Publicity Flier: PDF - December 19, 2008
Apollo 8: The 40th Anniversary
Panelists: Hal Beck, Rod Rose, Marty Jeness, Ken Young, John Llewellyn, Dr. Glynn Lunney, Dr. Christopher Kraft, and Emil Schiesser
Moderator: Marianne Dyson
Publicity Flier: PDF - March 10, 2008
Mars Exploration Rovers Spirit & Opportunity
Dr. Mark Adler, Chief Mission Concept Architect, Jet Propulsion Laboratory
Publicity Flier: PDF - February 21, 2008
Tour of Ad Astra Rocket Company
Hosted by Jared Squire
Publicity Flier: PDF - January 11, 2008
Space and Astronomy: Decade by Decade
Marianne Dyson, author and former NASA flight controller,
Publicity Flier: DOC - December 7, 2007
Report on Lunar Exploration Analysis Group (LEAG) Workshop and American Astronautical Society National Meeting
Dr. Larry Friesen
Publicity Flier: PDF - November 2, 2007
Apollo 13 Trajectory Reconstruction
Daniel R. Adamo
Publicity Flier: PDF - September 28, 2007
Werner Von Braun’s Long Road to Mars: A Story Within a Story
Dr. Albert Jackson / ESCG
Publicity Flier: PDF
Presentation: PDF - June 16, 2005
Aerospace on the FASTRAC: Student Built Satellites at the University of Texas
Dr. E. Glenn Lightsey / The University of Texas at Austin
Flier: PDF - May 19, 2005
Hierarchical Navigation Algorithms in Support of Mars Exploration
Robert H. Bishop / The University of Texas at Austin
Flier: DOC
Presentation: PDF - September 17, 2004
Trajectory Optimization from Euler to Lawden to Today
Christopher D’Souza / The Charles Stark Draper Laboratory
Flier: PDF
Presentation: PDF - March 24, 2004
Jules Verne and ISS, European Space Agency’s Automated Transfer Vehicle (ATV) First Rendezvous and Docking for a European Spacecraft
Brian Rishikof / Odyssey Space Research
Flier: PDF
Presentation: PPT, 3.25 MB - December 19, 2003
StarNav-1 Experiment on STS-107
Dr. Thomas C. Pollock / Texas A&M University
Flier: PDF - November 14, 2003
Spacecraft Fuel-Optimal Maneuvers, Apollo to Shuttle Return-to-Flight
Rob Hall / Draper Laboratory
Resources
- Please note that we have an excellent orbital debris presentation from our 2008 Annual Technical Symposium. The abstract is in the long form of the 2008 ATS program.
- Abstract (In ATS 2008 Long Form): http://www.aiaahouston.org/2008-annual-technical-symposium
- Presentation: PPT
- Movie Clips for presentation (please download & view separately):
News
News Articles Published Now and Then
[2024 02 03] February 3, 2024 – The International Astronautics Congress (IAC) will take place October 14-18, 2024, in Milan Italy. Al Jackson submitted an abstract a few days ago:
Apollo Lunar Module Aborts
A. A. Jackson, Associate Fellow of AIAA (AFAIAA), Fellow of the British Interplanetary Society (FBIS)
Triton Systems LLC, Houston, USA
Abstract: A typical Apollo lunar landing mission was divided into phases. Each phase would normally be preceded by a Go/No Go decision from Mission Control. Apollo mission design had a built in recovery from contingency, and the flexibility to rebound from unexpected emergencies. Outlined is a monomial Apollo mission. This presentation will only deal with the operational mission phases of the Lunar Module, powered descent, ascent and rendezvous with the Command Module. These were the prime phases of the Lunar Module’s mission. The safety of each of these stages was critical and needed careful planning. There was a dedicated subset of instrumentation and hardware for guidance, navigation and control for aborts of LM flight phases. Failure of a LM subsystem during powered descent, landing, surface operation, powered ascent and rendezvous had special planning and crew procedures. The evolution of each of the abort phases is reviewed here with as much detail that is reasonable.
Keywords: Apollo History, Spaceflight Contingency, Trajectory Design
[2022 11 12] Al Jackson is interviewed by Peter Schattschneider, the co-author of the ramjet paper below (2021 11 20). PDFs use these links for English and German versions.
[2022 10 02] The International Astronautical Congress (IAC) in Paris France (September 18-22, 2022) went well for Dr. Albert Allen Jackson IV (Triton Systems LLC). He travelled from Houston Texas USA to Paris France to enjoy the event. As noted below, the title of his paper was, “The Lunar Module Simulator: An Instructor’s Account.” [Douglas Yazell, 2022 10 02. Note: Today I also added an item on this list for Dr. Jackson’s presentation and paper at IAC 2019 in Washington DC. To see that item, scroll down or use this link.]
[2022 04 20] The International Astronautical Congress (IAC) accepted the submittal of Dr. Jackson (Triton Systems LLC) for the 73rd IAC, taking place this time in Paris France, September 18-22, 2022. His abstract, “The Lunar Module Simulator: An Instructor’s Account,” was accepted for a 12-minute oral presentation. Acceptance date: April 19, 2022.
[2021 11 20] Al Jackson has an article published in Acta Astronautica. This is the first time he published something in Acta Astronautica. Authors: Peter Schattschneider and Albert A. Jackson. Al Jackson is listed as Albert A. Jackson, Triton Systems, LLC, Houston TX, USA. Here is a link to the website of Triton Systems, LLC. The title of the research paper is “The Fishback ramjet revisited.” Acta Astronautica 191 (2022) 227-234. To describe Acta Astronautica, note that the Wikipedia article starts with this text, “Acta Astronautica is a monthly peer-reviewed scientific journal covering all fields of physical, engineering, life, and social sciences related to the peaceful scientific exploration of space. The journal is widely known as one of the top aerospace engineering journals. The journal was established in 1955 under the name Astronautica Acta, obtaining its current title in 1974, with volume-numbering simultaneously restarting at 1. The journal is published by Elsevier, sponsored by the International Academy of Astronautics.” The abstract for this research paper, “The Fishback ramjet revisited”: “In 1969, John Ford Fishback proposed a solution for the interstellar ramjet with magnetic scooping. With the exception of two papers published in the early 1970s, this model has not been revisited up to now for viability. Here, we analyze Fishback’s axial scoop field configuration. Computer simulations prove its functionality, albeit with absurdly long magnetic coils when reasonable thrust is to be achieved. Based on the Maxwell stress tensor we obtain a much lower upper bound for the cut-off speed at a given acceleration of the ramjet than published before. Our results indicate that there are severe engineering problems with the magnetic collection process. It is very unlikely that even Kardashev Civilizations of type II might build magnetic ramjets with axial solenoids.” Al Jackson presented a poster on this topic at the recent event in Tucson (below), the September 2021 Interstellar Symposia of the Interstellar Research Group (IRG). Here is a link for this Acta Astronautica research paper, “The Fishback ramjet revisted.” [Douglas Yazell, November 21, 2021]
[2021 10 06] AIAA Houston Section member Al Jackson is given the 2021 Eridani Award at the September 2021 Interstellar Symposia of the Interstellar Research Group (IRG) in Tucson Arizona. The 2nd Interstellar Research Group (IRG) Eridani Award ever given. Greg Matloff got the first; citation there was Eridani Professional Award for contributions to the interstellar community. Here is a link to an image which includes a snapshot of the award. [Douglas Yazell, October 6, 2021]
[2021 09 25] Al Jackson is in Tucson Arizona for a conference with the Interstellar Research Group, September 25-27, 2021. He and his co-author are presenting, “The Interstellar Ramjet: Engineering Nightmare.” The presentation slides are available here using this link. [Douglas Yazell, September 25, 2021]
[2020 04 19] My Spherical Quadrilateral. The Sine of the Beta Angle, a Function of 4 Euler Angles, Derived with 1 Vector Coordinate Transformation Equation. A Poster. [Douglas Yazell] The Beta Angle; the Angle Between the Solar Vector and the Orbit Plane. (See the Wikipedia beta angle article.) In other words, the beta angle is the angle between an line and a plane.
- I just cannot stop recreating this every few years. I was introduced to this in about 1990 as we did Space Station Freedom guidance, navigation & control work at the McDonnell Douglas building in Huntington Beach California USA. This was in our flight control simulation.
- The beta angle was a prominent input into our simulation. We varied beta in our matrix of test cases. From the beta angle and four other angles, the simulation calculated the right ascension of the ascending node (capital omega) of the orbit. That is equation (2) one or more of the posters below.
- This equation for the right ascension of the ascending node of the orbit, capital omega, was already in our simulation, and my first impression was that it was an ugly and big equation, but it contained only trigonometric terms we studied in high school (and BSEE undergraduate work, and my 1990-era graduate studies in engineering), so I derived it, with help from others and with patience and determination.
- My contributions included deriving the equation for the sine of beta (as a function of four other angles) using only principal axis rotations. The beta angle becomes a principal axis rotation angle just like those other angles. This provides additional insight compared to a more common derivation which uses a dot product of two unit vectors:
- The unit vector normal to the orbit plane pointing in the direction of the cross product of the satellite position vector crossed into the satellite velocity vector
- The unit Sun-pointing vector, or the unit solar vector
- Using a big monitor at home in the spring of 2020, I put a lot of information on a single chart. A colleague helping me with this called it a poster, a good name for it.
- I constantly make mistakes with this, so frequent updates will be needed.
- I should try (see below) sending this to the NASA engineer who wrote the charts and narrated the video used in the Wikipedia footnote (beta angle article), a NASA group whose acronym is ESC, so it becomes NESC in that footnote. The charts and videos are public domain. There are quite a few NASA documents and videos there available to the public.
- [2020 04 28] I updated and simplified the figure and equations below. Mr. Rickman answered my email note and provided links to the relevant public NASA website, “Here is the link to the top level NESC Academy page. There is a ‘Disciplines’ drop-down on the left hand side of the screen. If you click on this, you’ll see the major subject areas. Here is a link to the Passive Thermal page.” Here is a link to the charts and the video where Mr. Rickman derives the equation for the sine of beta as a function of four other angles.
- In my updated poster below, I am tempted to name that figure. It is a four-sided figure created from four great circles. It is not a spherical triangle, it is a spherical quadrilateral, and that is probably the name I will use. It does not appear in my 1945 spherical trigonometry book, “Plane and Spherical Trigonometry, with Tables,” by Frank M. Morgan, Director of Clark School, Hanover, New Hampshire, Formerly Assistant Professor of Mathematics, Dartmouth College. The publisher was American Book Company. Hardcover. Clothbound. I have no dust jacket.
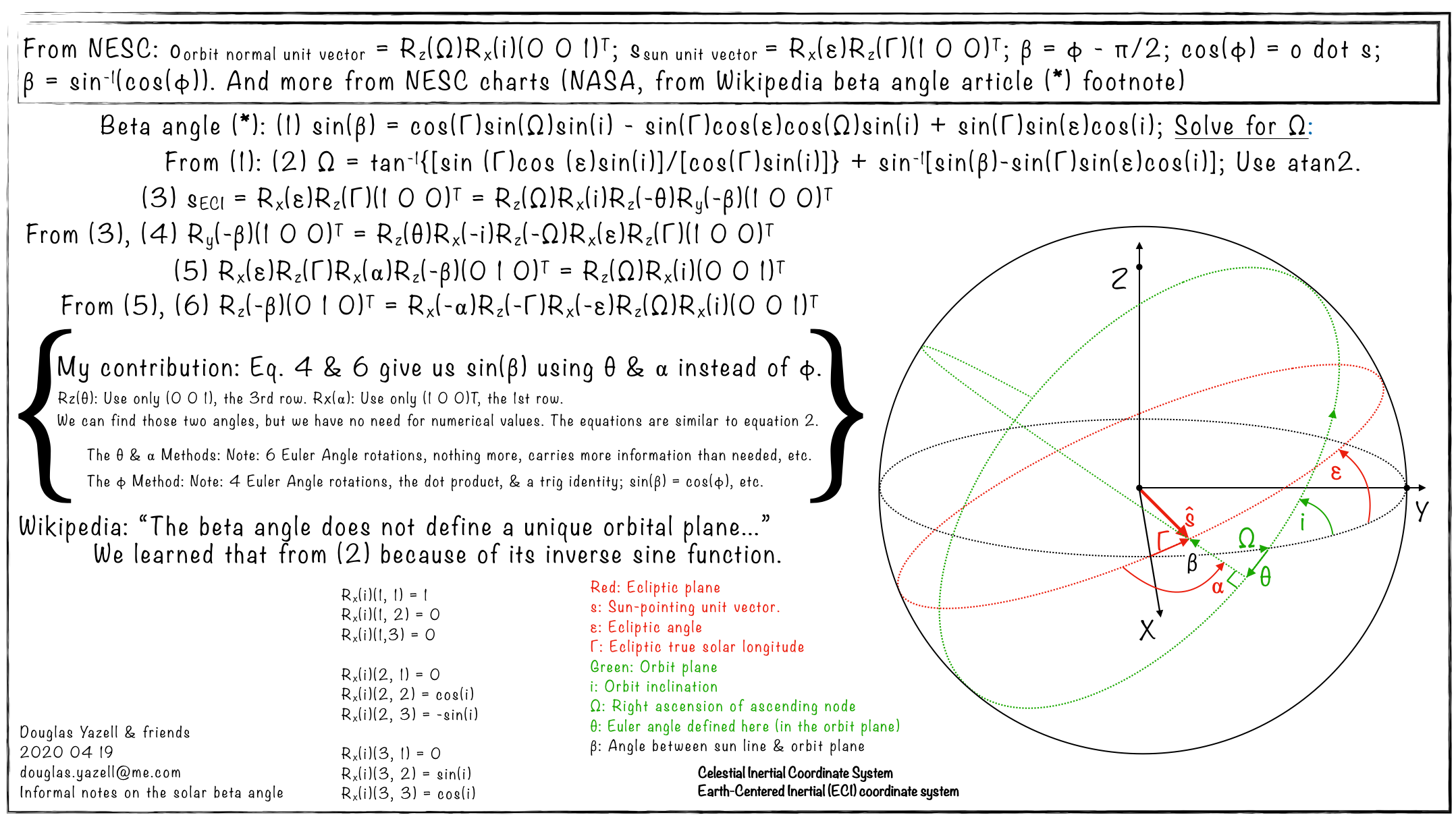
The beta angle. See the Wikipedia article. I created some new insights with a single figure and four equations. (Click to zoom.)
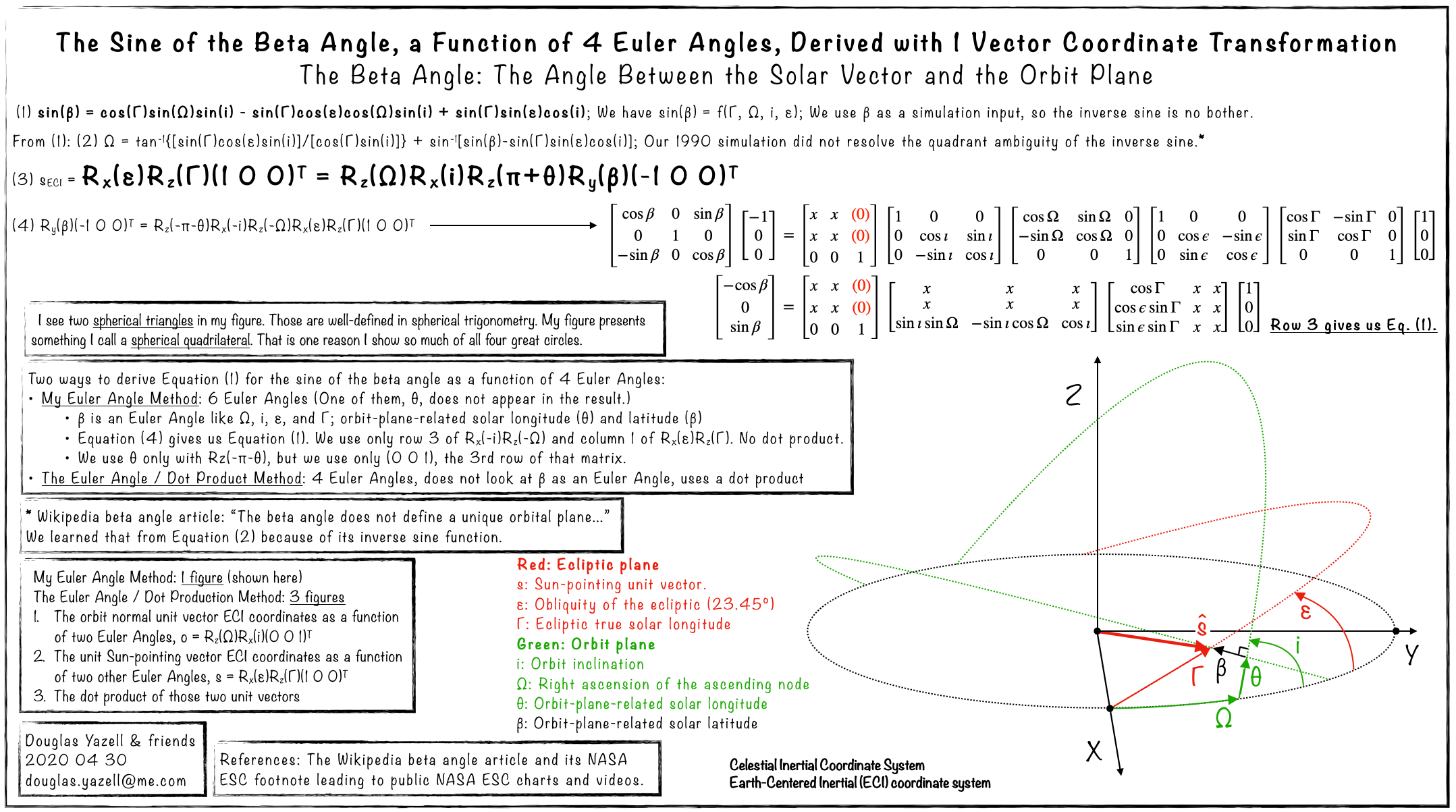
Above: The Solar Beta Angle, a Function of 4 Euler Angles, Derived from 1 Vector Transformation Equation. The Solar Beta Angle: the Angle Between the Solar Vector and the Orbit Plane. [Douglas Yazell, April 30, 2020] (Click to zoom.)
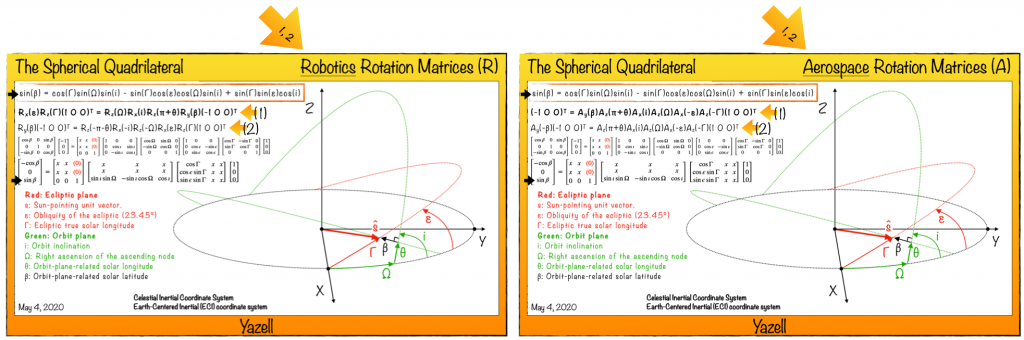
Robotics and Aerospace Rotation Matrices Compared Using My Spherical Quadrilateral and the Beta Angle. When using the aerospace (aviation) rotation matrices, I cannot even use ECI (Earth-Centered Inertial) as my fixed coordinate system, whether using the active or passive interpretation. (I was using the latter, but both work for these two posters.) The shortest route to my fixed coordinate system in that poster is through the obliquity of the ecliptic (23.45 degrees), then the ecliptic true solar longitude. [Douglas Yazell, May 4, 2020] (Click to zoom.)
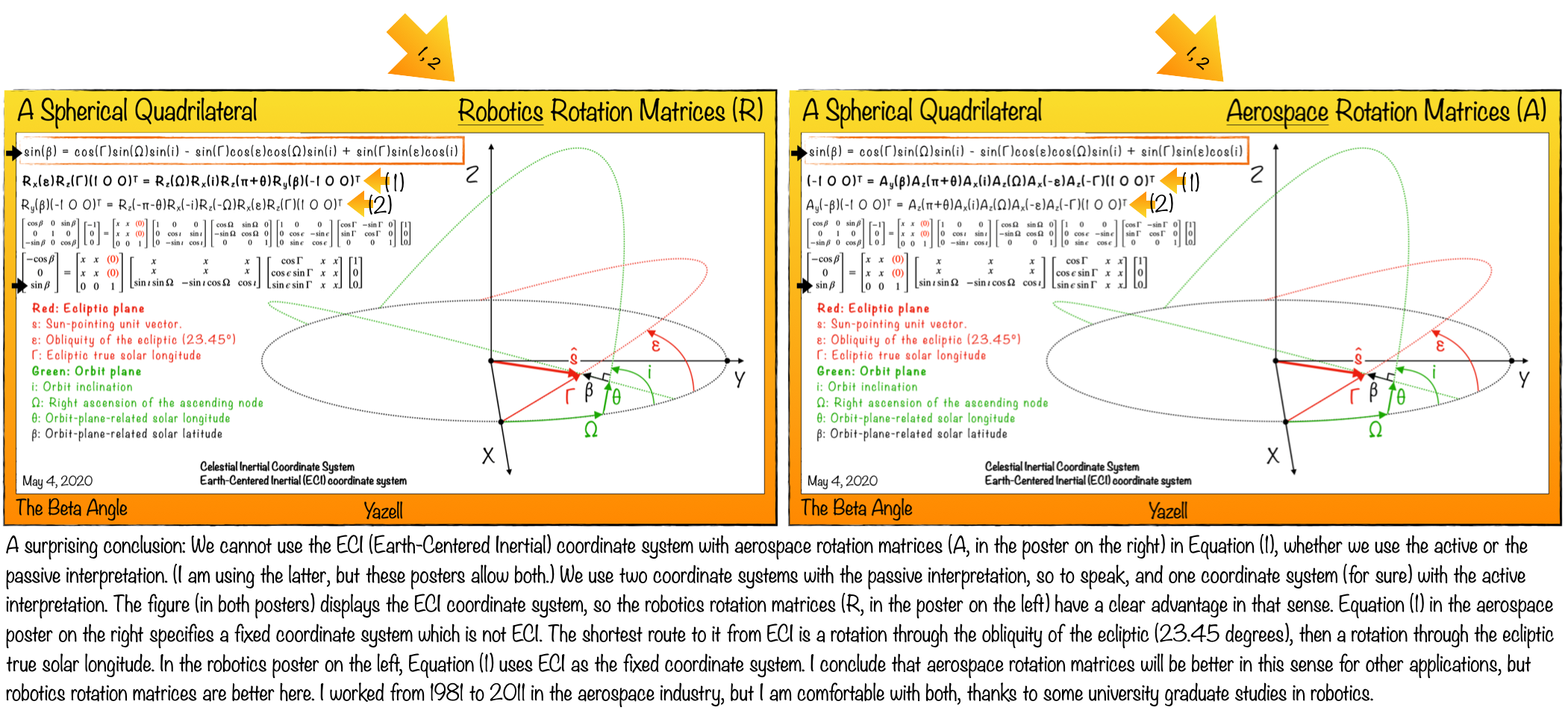
Above: A better caption. I found a surprise when I used aerospace rotation matrices in place of robotics rotation matrices. (Click to zoom.)
[2019 10 21] International Astronautics Congress (IAC) in Washington DC, October 21-25, 2019. Dr. Albert Allen Jackson IV presented a paper. Its title is, “The Mars Project 1948 to 1956,” by A. A. Jackson, Triton Systems LLC, USA, Houston Texas. The PDF is 13 pages. Univelt published this in 2022 as part of Volume 52 in the American Astronautical Society (AAS) History Series, in the form of a hardcover book. Abstract: “In 1948, Wernher von Braun conceived that he would inspire American interest in spaceflight by writing a novel about a mission to Mars. The underpinning of this story would be a very careful and detailed work up of the technical aspects. As the novel was being written, while at Fort Bliss, Texas, a technical appendix was assembled with help of six colleagues from Peenemünde. Examined here are some technical aspects of this Mars mission, in particular the evolution of the vehicles and their technical realization. What started as the design of a mission to Mars evolved into the large-scale concept of manned spaceflight, the design of earth to orbit ferry ships, a space station to support orbital assembly of fleet to Mars. The architecture for a Mars mission provided the method for explorationa of the Moon. There was a steady evolution of vehicle design and mission configuration until a final expression was presented in 1956.” [Update created 2022 10 2, Douglas Yazell]
[2017 01 02] Published here January 2, 2017. Adamo Astrodynamics Archive Copied to Our Web Page. (It is a pleasure to connect Snoopy and the Red Baron to this subject.) Here is a link to the PDF version of the JPEG image below. [Update January 7, 2017: Please click here to see the the news about the updated URL for the AIAA copy of this archive. The news article below (JPEG and PDF versions) does not need updating, since www.aiaahouston.org/astrodynamics_technical_committee/#ATIG will lead to www.aiaahouston.org/adamo_astrodynamics.]
[2016 08 14] August 14, 2016 A Green Flash at Sunrise Dan Adamo (adamod at earthlink dot net) emailed a sunrise green flash photo to one of us. He is now retired and living in Oregon instead of the Houston area in Texas, and the photo shows Mount Hood. He allowed us to publish the photo here, along with that part of his email note: “With the Sun moving south to about +20.5 deg declination, it was time to take shots of Mt. Hood sunrises from my location this week. I’ve attached one capturing yet another green flash as the first rays of sunlight reached me over the mountain’s north slope on July 20. During less than 2 seconds on this occasion, my visual impressions were of intense blue fading to green and yellow. It’s an amazing sight, and it fell 13 months plus a day before 2 minutes of total solar eclipse will favor my abode. Hope the weather’s as nice… -Dan”. Link: IMG_1961.jpg, 354 KB.
[2015 03 05] March 5, 2015 100 YEAR STARSHIP ESTABLISHES EU HUB IN BRUSSELS TO ADVANCE SPACE, SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY INITIATIVES WITH EUROPEAN PARTNERS
Read the press release using the 100YSS press page link and the press release date (March 5, 2015).
[2015 02 26] February 26, 2015 French National Center for Space Studies (CNES) at the First International Academy of Astronautics (IAA) Climate Change Conference
[This CNES press release (see this link) explains that climate change is an aerospace subject and explains that climate change is an astronautics subject. In fact, it mentions that of 50 variables used to define climate, 26 of them can be measured only from space.]
[Jean-Yves Le Gall, President of the French National Center for Space Studies (CNES), opened the first conference on climate change and disaster management, organized by the International Academy of Astronautics (IAA) and the International Institute of Space Law (IISL), which was held from February 26 to 28 in Kovalam, Kerala, India.]
This conference, co-organized by the IAA, IISL, and the KSCSTE (Kerala State Council for Science, Technology and Environment), focuses mainly on the many contributions of space in the understanding of climate change. Specifically, of 50 variables used to define the climate, 26 can only be measured from space, demonstrating the importance of this area to assess the changing climate.
The IAA is a non-governmental organization recognized by the United Nations, which brings together 1,200 international experts in astronautics from about 75 countries. Its objectives are to promote the development of astronautics for peaceful purposes and to honor those who are distinguished in astronautics. It promotes international cooperation for the advancement of aerospace sciences.
Invited to deliver the keynote address, Jean-Yves Le Gall, Chairman of CNES, first emphasized the historic challenge facing the space to preserve the future of the planet: “Space agencies can not answer all questions but without space agencies, nothing will be done. ” In this context, he has said that, “global Earth observations were indispensable to understand climate change and to make the most appropriate responses.”
Then he emphasized, “the important role of the international program GCOS (Global Climate Observing System)”, recalling that, “Europe, and specifically France, were actors in the forefront in climate observation.” In this area, the programs named Copernicus, Jason, SWOT and Merlin are of major importance. Cooperation between India and France is already very productive, notably with missions Megha-Tropiques and Saral-AltiKa.
“The future Conference of Parties 21 (COP 21, a meeting of the IPCC, the International Panel on Climate Change, associated with the United Nations) to be held in Paris in December, the importance of the IAA and its voice in the world, and international cooperation in space are elements and events that must converge to a general awareness for the protection of the planet through the regular collection and continuous analysis of data from space technology,“ he said. He concluded by stressing the need to mobilize all actors because, quoting the Secretary General of the United Nations, “There is no Plan B because there is no planet B.”
Translation from French to English by Douglas Yazell, with excellent help from http://translate.google.com.
[End of AIAA Houston Section astrodynamics technical committee web page, July 27, 2016]